INTRODUCTION
The epidemiological, immunological, and clinical aspects of Chagas disease in the Brazilian Amazon differ from those in other Brazilian regions in several aspects. Firstly, the main triatomine vector in the Brazilian Amazon belongs to the genus Rhodnius1 whereas Triatoma is prevalent in other regions2,3. Secondly, as disease transmission does not typically occur in dwellings in the Brazilian Amazon, Chagas disease is sometimes considered an occupational disease in this region4. However, acute outbreaks due to contaminated food have being commonly reported in endemic areas of the Western Amazon5. Thirdly, the chronic phase is characterised by low morbidity2, with the exception of some fatal cases resulting from dilated cardiomyopathy in autochthonous patients from the Middle Negro river basin6,7.
Chagas disease is caused by the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi and is naturally transmitted through triatomine haematophagous bugs1. Rhodnius brethesi is a sylvatic triatomine originating from the native palm tree piassaba Leopoldinia piassaba in the Barcelos region, Amazonas State, Brazil4,8. The epidemiological aspects of Chagas disease transmission are characterised by the absence of vector domiciliation, suggesting that this condition is an occupational disease4. However, uncontrolled deforestation in the Amazon tends to increase the house invasion by sylvatic triatomines and the risk of T. cruzi infection transmission9. Despite the high prevalence, some clinical studies have reported that the acute phase is marked with high morbidity, including some fatal cases of dilated cardiomyopathy6. However, the results of several studies based on clinical and electrocardiographic analyses of seropositive Chagas disease patients from the Amazon basin suggest low morbidity, likely reflecting circulating T. cruzi strains and low parasitaemia7,10,11,12,13.
Many immunoregulatory mechanisms have been proposed for T. cruzi infections, including those that involve regulatory T cells and regulatory cytokines14. Patients with cardiac Chagas disease develop a strong immune response against the parasite, showing high levels of interferon gamma and low levels of interleukin-1015. With this background, it is important to examine whether low morbidity of the Chagas disease in the Brazilian Amazon is due to downregulation of the Th1 immune response, which maintain the infected individual in a long asymptomatic period.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
STUDY AREA
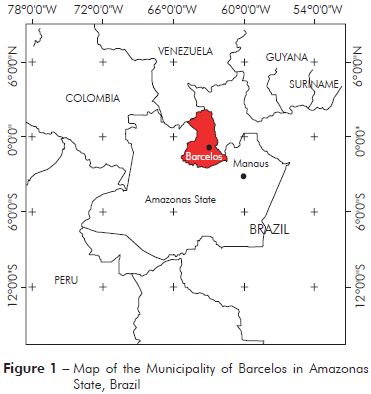
The Municipality of Barcelos (S00o42’/W62o58’) covers an area of 122,476.123 km2, located at 490 km from Manaus, Amazonas State (Figure 1). In 2010, according to the Brazilian Institute for Geography and Statistics (IBGE)16, this region contains a population of 25,718 individuals, with 14,561 residents in the rural area (56.6%) and 11,157 (43.4%) residents in the Municipality. The economy of Barcelos is based on extractivism activities, fishing, subsistence agriculture, and tourism. Piassaba (Leopoldinia piassaba) fibres obtained through the extractivism activity are important for rural populations as a source of economic income. The fibres of this palm are used in the manufacture of handicrafts, baskets and brooms.
SAMPLING POPULATION
The present study was conducted in the residential district of the Municipality of Barcelos as an observational and cross-sectional analysis of 155 native inhabitants and their households. A survey of the epidemiological and socioeconomic aspects, such as occupation, recognition of triatomines, and other risk factors associated with Chagas disease, was conducted. The study was approved by the Ethical Review Board of the Universidade Federal do Amazonas (approval number CAAE#0139.0.115.000-10) on June 16, 2010.
BLOOD COLLECTION AND SEROLOGY
After obtaining written consent, blood sample was collected from each participant through venipuncture into heparinised vacuum tubes. An aliquot of total blood was used for flow cytometric analysis based on the expression of surface markers. Subsequently, the blood samples were centrifuged for 10 min at 3,000 rpm. The plasma samples were analysed for the presence of IgG antibodies using an immunoenzymatic assay (ELISA) and the indirect immunofluorescence method (IIF). For ELISA, the Chagas test ELISA III kit (Abbott Laboratórios do Brasil LTDA, São Paulo, Brazil) was used. All assay procedures were automated, and the ELISA reactions were measured at 450 nm using an Asys Expert Plus microplate reader. The reactive, inconclusive and undetermined samples were subjected to IIF analysis. These analyses were conducted using anti-human globulin anti-IgG (Imuno-CON Chagas®; Wana Diagnostica, São Carlos, Brazil) at a 1:40 dilution. Individuals seropositive for both methods (ELISA and IIF test) were considered as positive for chagasic infection.
MEASUREMENTS OF CYTOKINES
Serum cytokines-related Th1/Th2/Th17 were measured using a Cytometric Bead Array Kit (CBA, BD Pharmingen, San Diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, samples and standards were incubated with capture beads for 1 h at room temperature, followed by incubation with phycoerythrobilin-labelled IL-2, IL-4, IL-10, IL-17, IFN-γ and TNF-α detection antibodies for 2 h at room temperature to achieve complex formation. Subsequently, the samples were washed, and the mean fluorescence intensity was detected using flow cytometry (FACSCaliburTM, Becton Dickinson, CA, USA). The data were analysed using BD Cytometric Bead Array analysis software.
FLOW CYTOMETRY
The blood samples were stained with anti-CD8, anti-CD4, anti-CD3, anti-CD69 and anti-CD25 antibodies labelled with phycoerythrin or fluoresce in isothiocyanate at concentrations titrated for optimal staining. The cell suspensions and fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies were incubated for 15 min at room temperature in the dark. After incubation, the cell suspensions were incubated with a fixative in lysing solution for 10 min, followed by centrifugation for 7 min at 1,300 rpm. The immunophenotyping was analysed by the fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACSCaliburTM, Becton Dickinson, CA, USA) according to fluorescence intensity.
STATISTICS ANALYSES
The values were tested for normality and equal variance (Kolmogorov-Smimov and F-test, respectively). Based on serological reactivity (ELISA and IIF tests), the comparison between positive and negative groups was assessed using the Mann-Whitney U test. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) was used for the analysis of each data group (e.g., seroepidemiology, cytokines or immunophenotyping). The first and second components were used to obtain information from the PCA matrix data. However, the relationship among serology, epidemiology, cytokine profiles, and cellular phenotypic patterns were examined using a redundancy analysis (RDA). Specifically, a matrix of predictor variables (seroepidemiological data) was used to quantify the variation in a matrix of response variables (cytokine and cellular phenotypic profiles). Monte Carlo permutation tests (499 times) were performed to determine the statistical validity of the association between seroepidemiological data and immunological patterns. All statistical analysis were considered significant at p < 0.05. The PCA and RDA were performed using the software package for multivariate data analysis Canoco for Windows v.4.5.
RESULTS
SEROLOGY AND CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDIED POPULATION
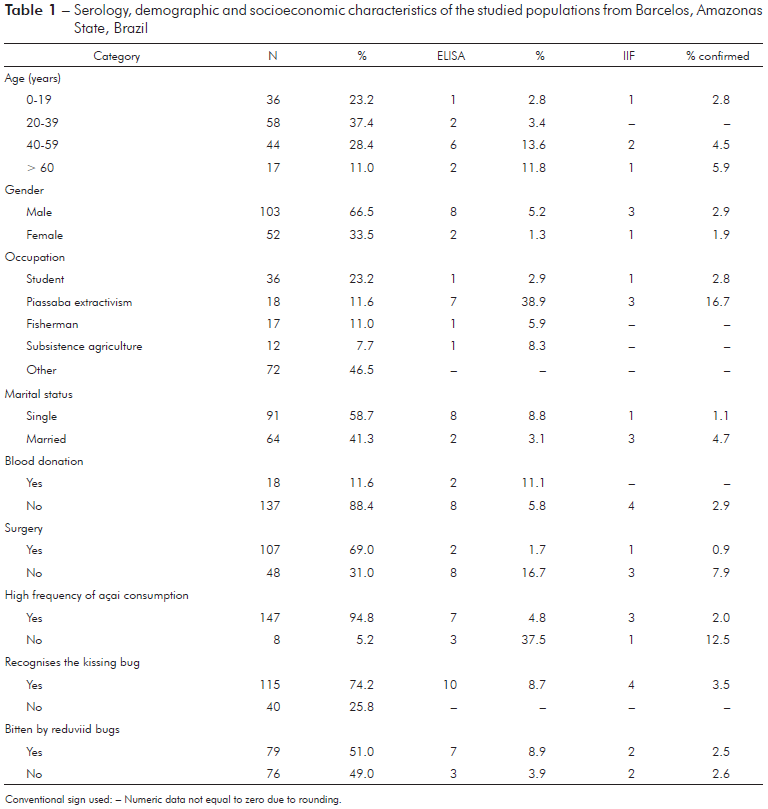
In the present study, ten (6.5%) of the 155 samples were reactive to the ELISA test (Table 1). The IIF method was applied to these ten samples, only four samples were reactive for chagasic infection, and 2.6% seroprevalence was calculated. One of the individuals (female) showing chagasic infection was a 12-year-old student (non-piassaba extractor), while other three individuals has been working almost exclusively in piassaba extractivism. The positivity rate of non-piassaba gatherer was 0.7% (1/137). Among the 18 who worked as piassaba gatherers, seven were seropositive according to ELISA (~39%) and three individuals were seropositive according to IIF (16.7%), and all of these individuals were male. Regarding seropositivity according to the IIF test, all individuals were considered native to the region and worked at the Aracá river, an important piassaba extractivism region in the Middle Negro river. Moreover, all individuals with reactivity to chagasic infection identified triatomes as kissing bugs. However, only two individuals reported being bitten by these bugs.
Conventional sign used: - Numeric data not equal to zero due to rounding.
Table 1 - Serology, demographic and socioeconomic characteristics of the studied populations from Barcelos, Amazonas State, Brazil
In the PCA model, which included occupation, marital status, gender, surgical procedures, blood donation, recognition of the reduviid bugs, triatomine bug bites, and serology, the first component explained 75.1% (Eigenvalue = 2.8) and the second component explained 11.2% (Eigenvalue = 0.4) of the total variance. The extraction of piassaba explained 94.3% of component 1, and this variable was also associated with male individuals with high levels of anti-T. cruzi IgG, who reported being bitten by triatomine bugs.
PLASMA CYTOKINES
The levels of all cytokines did not differ between seropositive and seronegative individuals (Table 2), except the levels IFN-γ, which were significantly lower (Mann-Whitney Rank test, p < 0.05) in seropositive than in seronegative individuals. The Principal Component Analysis (PCA), based on the variance and covariance matrix of the Th1/Th2/Th17 cytokines, revealed that the first component explained 64.6% and the second component explained 16.4% of the total variance. Component 1 primarily reflected individuals with high levels of TNF-α and IL-6, while component 2 was associated with individuals with high values of IL-2, L-17, and IFN-γ (Table 3).
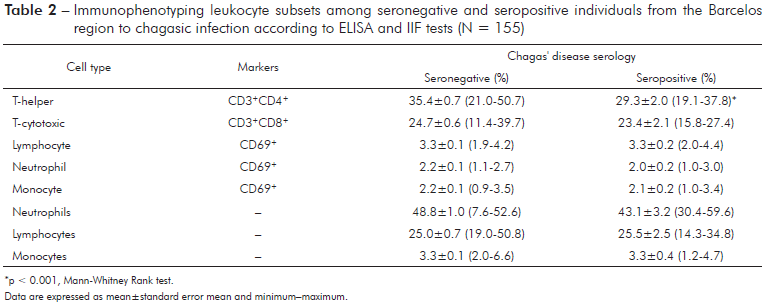
*p < 0.001, Mann-Whitney Rank test. Data are expressed as mean±standard error mean and minimum-maximum.
Table 2 - Immunophenotyping leukocyte subsets among seronegative and seropositive individuals from the Barcelos region to chagasic infection according to ELISA and IIF tests (N = 155)
IMMUNOPHENOTYPING
The percentage of lymphocytes (CD3+CD8+ and CD69+), neutrophils (CD69+), and monocytes (CD69+) was not significantly different between seronegative and seropositive groups (Table 2). However, the percentage of CD3+CD4+ lymphocytes was significantly (p < 0.001) lower in seropositive individuals compared with individuals seronegative for chagasic infection. In the PCA model, component 1 explained 69.9% of the variance, while component 2 explained 18.4%. Neutrophils and lymphocytes were most important variables contributing to axis 1, while CD3+CD8+ and CD3+CD4+ lymphocytes contributed to axis 2.
SEROEPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS
A diagram of the redundancy analysis is shown in figure 2. This ordination method is an extension of the regression analysis for the simultaneous examination of several variables. In this model, the explanatory variables (e.g., serology, piassaba extractivism, blood donation, gender, marital status, and surgical procedure) were coded as dummy variables, while the response variables (e.g., cytokines and immunophenotyping) were used as a primary data set. When both cytokines and immunophenotyping as response variables, the sum of all canonical eigenvalues showed that 57.8% of the total variation in the immunological response could be explained by explanatory variables (seroepidemiological data). However, when variations were partitioned (cytokines or immunophenotyping), the seroepidemiological variables contributed to 36.3% of the total variation when the cytokines were considered as response variables and immunophenotyping was considered as a covariable. The ordination diagram indicates that individuals with high levels of antigens to chagasic infection showed low percentages of lymphocytes and monocytes and low levels of Th1 cytokines (INF-γ and IL-2). However, the percentage of neutrophils was increased according to the ELISA data for Chagas disease serology.
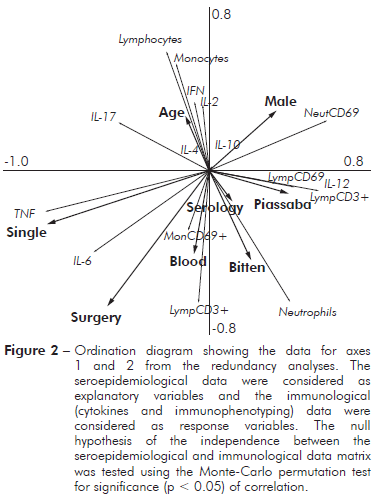
Figure 2 - Ordination diagram showing the data for axes 1 and 2 from the redundancy analyses. The seroepidemiological data were considered as explanatory variables and the immunological (cytokines and immunophenotyping) data were considered as response variables. The null hypothesis of the independence between the seroepidemiological and immunological data matrix was tested using the Monte-Carlo permutation test for significance (p < 0.05) of correlation.
DISCUSSION
Since the early 80’s when the first autochthonous case of Chagas disease was reported in the Western Brazilian Amazon (Municipality of São Paulo de Olivença, State of Amazonas)17, several studies were conducted to describe the prevalence4,7, acute outbreaks5,18 and cardiomyopathies6,14,19 associated with infection by T. cruzi.
Except acute outbreaks through oral transmission, Chagas disease in the microregion of Rio Negro (Municipality of Barcelos) typically occurs in individuals who work in extractivism activity or subsistence agriculture near piassaba areas9. Approximately 14% of Barcelos population participated in the extraction and trade of piassaba20. In the present study, the proportion of workers involved in the piassaba extraction was 11.6%, consistent with previous reports. The risk of transmission enhance by the presence of piassaba palm near households, in which specimens of Rhodnius robustus and R. pictipes inside houses have been found21.The amount of piassaba gatherers increases as well as several fishermen have migrated to piassaba extraction due to the drastic decline of the ornamental fish trade in this area, as a consequence the number of chagasic infections cases might increase in the future.
The four (both ELISA and IIF methods) or ten (only to ELISA test) cases identified as reactive for chagasic infection among 155 autochthonous people from the Municipality of Barcelos suggested 2.6 to 6.5% prevalence, respectively. This result is consistent with previous studies conducted in the population of the studied area, showing a prevalence of 1.9 to 6.8%2,4. Herein, among the four positive cases confirmed through ELISA and IIF analyses, a single case involving an autochthonous 12-year-old female individual (student) and three cases of male piassaba gatherers, over 50 years old. Consistent with other finding4, clearly, the piassaba extractivism in the Barcelos region constitutes a risk factor for Chagas disease.
Despite the high prevalence, several clinical studies have reported that the acute phase is marked with high morbidity, including some fatal cases of dilated cardiomyopathy6,19. It has been reported that Chagas disease in the Middle Negro river has a clinical profile of low morbidity and mortality in the chronic phase12. The biological diversity of circulating T. cruzi has an important role in the clinical, immunological and epidemiological features of Chagas disease in the Amazon basin12,13,18. It has been suggested that the low parasite load and low levels of serum IgG anti-T. cruzi might reflect the discrete typing units of T. cruzi in this case TcI prevalent in the Brazilian Amazon, instead of the TcII, TcV and TcVI genotypes predominant in the domestic transmission cycle of the South Cone in the South America, where chagasic patients are characterised by higher parasitaemia, virulence and pathogenicity12. The outbreaks of acute Chagas disease in the Amazon region have been associated with TcI13. However, recent studies suggest an emergency of a new epidemiological profile in Central Amazonia based on isolates from the outbreaks typed as TcIV18. It is likely that infection by particular T. cruzi strains may result in different immunological profiles.
Many immunoregulatory mechanisms have been proposed for T. cruzi infection, including those that involve regulatory T cells and regulatory cytokines22,23. Cytokines play a major key in the control of the immune response to T. cruzi infection24,25. It has been suggested that during the chronic phase cardiac Chagas disease patients show uncontrolled INF-γ production in the heart, promoting the cytolytic destruction of the myocardium23. However, during the acute phase of Chagas disease, this cytokine acts to eliminate the parasite14,15. In the present study, INF-γ secretion was down-regulated in seropositive individuals from the Barcelos region. The low levels of circulating INF-γ might reflect the reduced percentage of T-helper CD3+CD4+ lymphocytes. This profile is consistent with the idea that in chagasic infection, the majority of INF-γ producers were CD3+CD4+ cells15. As INF-γ is a key factor associated with the development of severe cardiomyopathy, the phenotypic and cytokines profiles of seropositive individuals from the Barcelos region suggests the downregulation of the Th1 immune response, maintaining infected individuals in a long asymptomatic period of occasionally more than 20 years.
Several cases of dilated cardiomyopathy were reported in autochthonous patients with chronic chagasic infection from the municipalities of Barcelos and Santa Isabel do Rio Negro6,26. Furthermore, it was reported that the frequency of chronic cardiomyopathy associated with Chagas disease in autochthonous individuals from Amazon basin was 8.1%19. With this background, it is important to examine whether the exacerbated Th1 immune response against T. cruzi antigens, characterised by high levels of INF-γ secreted from CD3+CD4+ cells and low levels of IL-10 are demonstrated in individuals with cardiac Chagas disease in the Brazilian Amazon.
CONCLUSION
Chagas disease in the Central Amazonia is clearly associated with piassaba extractivism. The major alterations observed in the seropositive individuals were lower INF-γ cytokines, consistent with low percentages of CD3+CD4+ cells. This mechanism might modulate Th1-like immune responses, maintaining a balance between parasitism control and cardiac integrity during a long asymptomatic chronic period of this disease.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We wish to thank all autochthonous individual from Municipality of Barcelos who participated in this study, the staff of Fundação de Hematologia e Hemoterapia do Amazonas. We would like to thank Juliana L. V Lameiras, Maria Samilly P. Melo and Allyson G. Costa for their support in collecting and processing the blood samples. The authors would also like to thank Dr. José Fernando Marques Barcellos for his helpful discussion and revision of the manuscript.